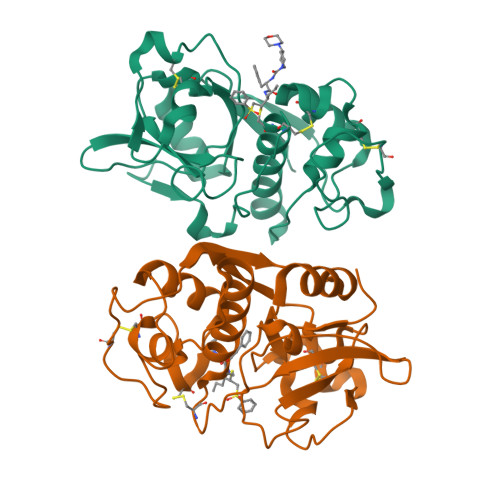
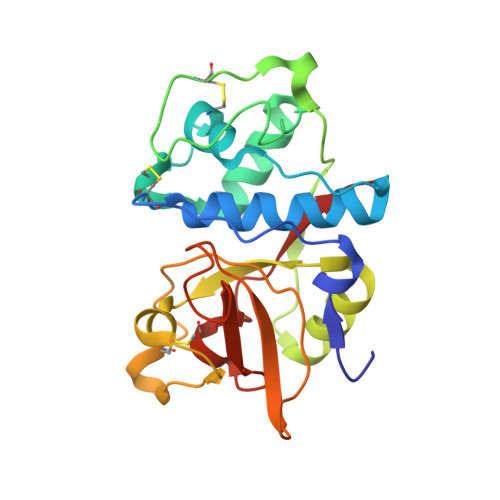
The crystal structure of human cathepsin F and its implications for the development of novel immunomodulators
Somoza, J.R., Palmer, J.T., Ho, J.D.(2002) J Mol Biology 322: 559-568
- PubMed: 12225749
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00780-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M6D - PubMed Abstract:
Cathepsin F is a lysosomal cysteine protease of the papain family, and likely plays a regulatory role in processing the invariant chain that is associated with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II. Evidence suggests that inhibiting cathepsin F activity will block MHC class II processing in macrophages. Consequently, inhibitors of this enzyme may be useful in treating certain diseases that involve an inappropriate or excessive immune response. We have determined the 1.7A structure of the mature domain of human cathepsin F associated with an irreversible vinyl sulfone inhibitor. This structure provides a basis for understanding cathepsin F's substrate specificity, and suggests ways of identifying potent and selective inhibitors of this enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal and Structural Chemistry, Celera, 180 Kimball Way, 94080, South San Francisco, CA, USA. john.somoza@elera.com